What exactly is Industry 4.0 technology?
Industry 4.0 can be defined in many ways. In simple words, it entails making technology, not management by people, the core driver of the manufacturing process. Here, smart devices communicate with each other to make desicisons and fundamentally change the way entire industrial value chain is organized and controlled. Lest we forget, this is made possible only through combination of two great changes: The changes in machines, and the change in the mindset of people.
A perspective on what really makes Industry 4.0 work
A change in technology
An aircraft flying in the sky is not just an object made of one technology. It involves turbine engines, aerodynamic design principles, even a degree of metallurgy to dsign the body. Then, there are airports where air traffic controls ans communications come into play.
If you consider just the turbine engine, it took hundreds of years to arrive at a stage where it could be used to fly an air craft. Air traffic control, telecommunications, geo location, logistics and technologies in many other areas had to converge to make commercial aircraft industry possible. The same is the case with Industry 4.0.
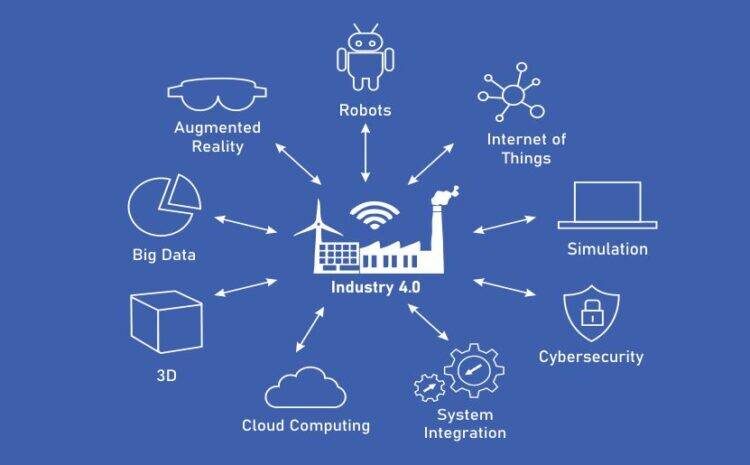
Industry 4.0 is not just one technology but a convergence and amalgamation of several technologies that have matured over time.
The technologies that comprise Industry 4.0
Big Data
Big Data involves prying out hitherto unseen patterns, correlations, and insights about customer preferences from large and diverse datasets.
How it helps?
Significantly improve service quality
Uncover new opportunities
Enable quick decision-making with real-time data
Example
Identify faulty products in the early stages of production process so that the costs are saved and final product quality improves.
Robotics
Robots are generally equated with a high level of mechanization, and that’s not entirely wrong. But in industry 4.0, robots are becoming smarter. They are more autonomous and flexible.
How it helps
Unprecedented levels of productivity
Increased competitiveness
Near zero downtime
Example
Robots equipped with cameras and advanced control systems can assemble entire products alongside humans.
Virtual simulation
Using computer simulation to design and test products and distribution systems.
How it helps
Reduced machine setup time
Machines optimized even before the production starts
Faster testing resulting in speedy innovation
Error-free products
Example
Data from phyysical machining processes is used to simulate machining of parts. This eliminates errors and cuts the machining time by more than half.
IIoT
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is essentially a bridge that connects people, machines, and data. IIoT involves using communication technology to connect all devices across the shop floor. The system then works to collect and analyse information to generate new insights.
How it helps
Products can be infused with computing capability to communicate with each other as well as controllers
Improved connectivity boosts efficiency
Data-enabled predictive maintenance saves costs
Improved workplace safety
Example
As products and machines communicate with each other, the machines know in advance as to which action needs to
be performed to repair or finish an unfinished product
Cloud computing
In cloud computing, data is stored, accessed, and analysed using the limitless capacity of the Internet. Cloud computing enables rapid scaling and real time informatin support for a multitude of devices.
How it can help
Processes that require sharing vast amount of data are made easier
Significantly reduced reaction time
Increased capability to store and analyse vast amount of data
Example
Cloud computing is considerably improving collaboration between manufacturers and distributors, brining more speed and reliability in complex global supply chains
3D printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a key technology in prototyping of products. It has evolved over a span of 30 years to arrive at its current state.
How it helps
Easy production of lightweight products with complex designs
Improved inventory management
High savings in costs
Example
3Dprinting is allowing aerospace industry to implement new designs that make aircrafts more lightweight and help cut raw material costs.
Augmeted reality
AR is currently used in areas such as locating products in wearhouses and locating parts for product repair. AR devices are delivering instructions to field workers in real time, making work procedures easier and faster.
How it helps
Improved decision-making process
Real time workflow instructions
Better speed and accuracy in product location and repairs
Example
AR-enabled smart glasses can tell workers where parts of a product are located and where to insert them in product
assembly pr repairs. This eliminates misunderstanding that might result from workflows on paper and make the process easier and faster for the worker.
Cybersecurity
As factories become smart with Industry 4.0 capabilities, system, security of cyber-physical machines is vital. Cyber security is an area that encompasses all technologies and measures that protect business data, networks and smart machines from cyber attacks.
How it helps
Better management of access to information
Secure and reliable communications
Improved reliability of systems and networks
Example
Recently a ransom cyber attack on the oil pipeline affected several regions creating shortage of fuel and panic buying.
Threat to cyber security is real and widespread with key infrastructure assets connected to the internet.
Conclusion
As Information Techonlogy integrates with Operational Techonlogy, the toolset for Industry4.0 is growing rapidly. Autonomous machines are eliminating downtimes and production errors, managing complex supply chains, and making the industry more competitive than ever. However, successful implementation of these tools requires a change in mindset. The way we collect, protect and share data, and make decisions must change. That’s when we truly benefit from Industry 4.0.
